India is a vast land brimming with talented and creative people of diverse backgrounds. There are many wonderful things India has introduced to the world. From 0 to the world’s first university, from Snakes & Ladders to shampoo, India has been quite the Santa Claus.
Here are 20 things you did not know were introduced to the world by India.
1. India gave the world its first university – Takshashila University
As early as 700 B.C., there existed a giant University at Takshashila, located in the northwest region of India. It had 300 lecture halls, laboratories, a library and a towering observatory for astronomical research. A Chinese traveler, Hien Tsang wrote in his diary that it had 10,000 students and 200 professors.

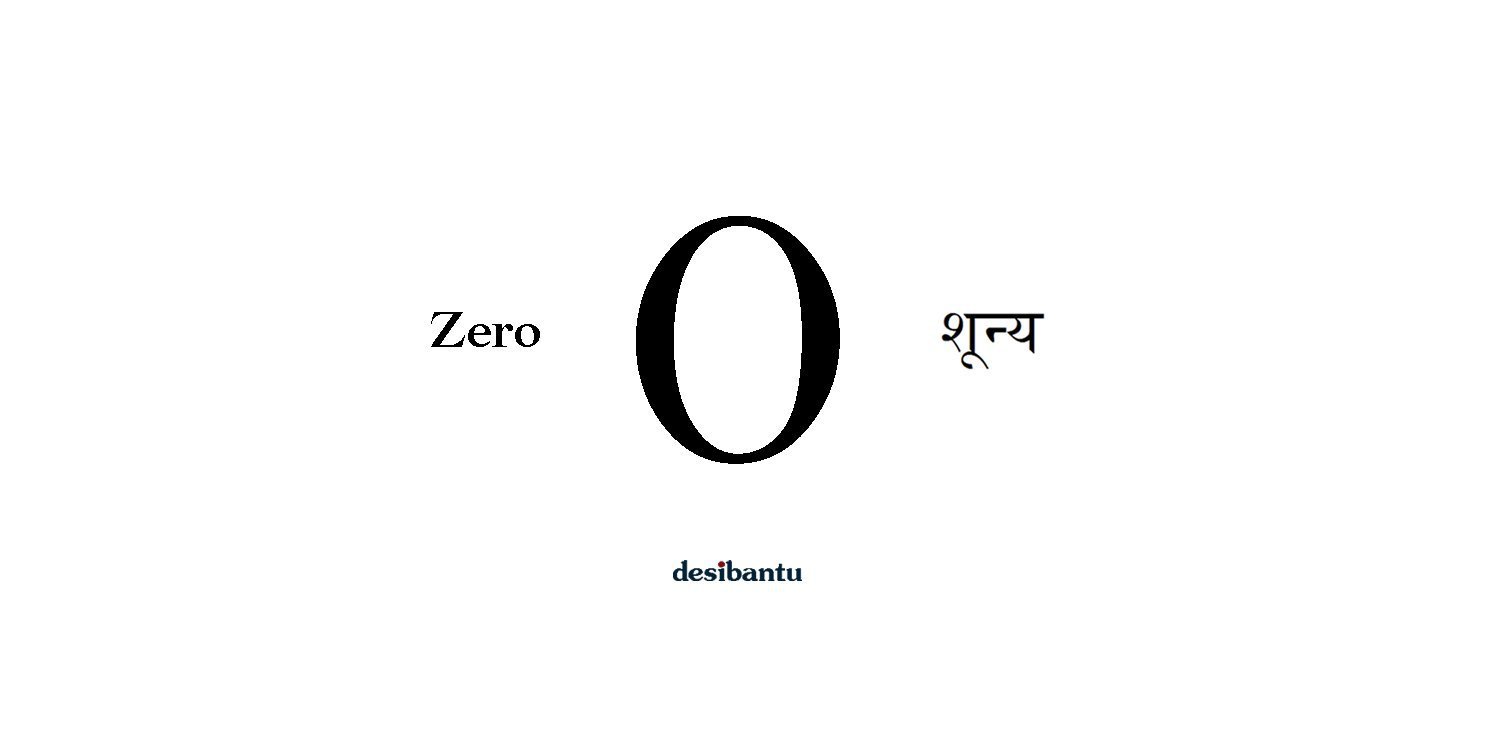
2. India gave the world the numeral, Zero
Although Babylonians used zero to signify the ‘absent’, Indians were the first to use the zero as a symbol and in arithmetic operations.
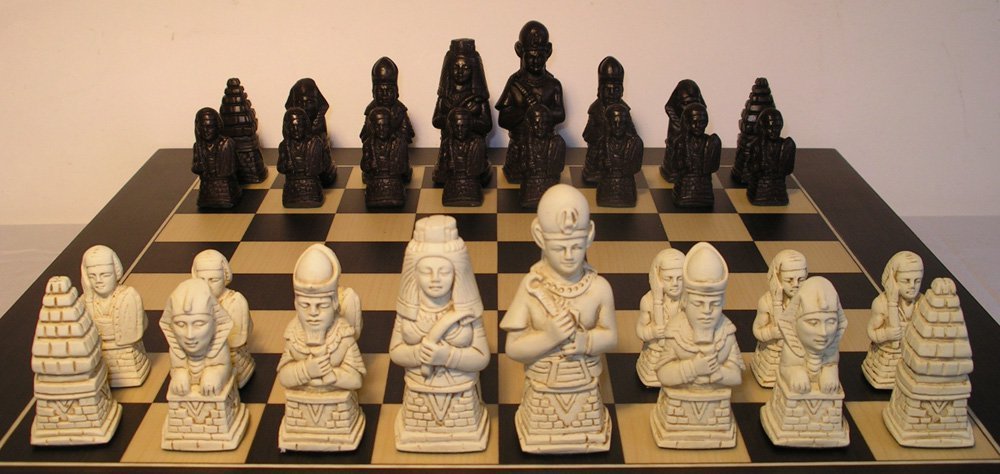
3. The game of C hess originated in India
Chess is believed to have originated in Eastern India , c. 280 – 550 CE, in the Gupta Empire , where its early form in the 6th century was known as chaturaṅga.

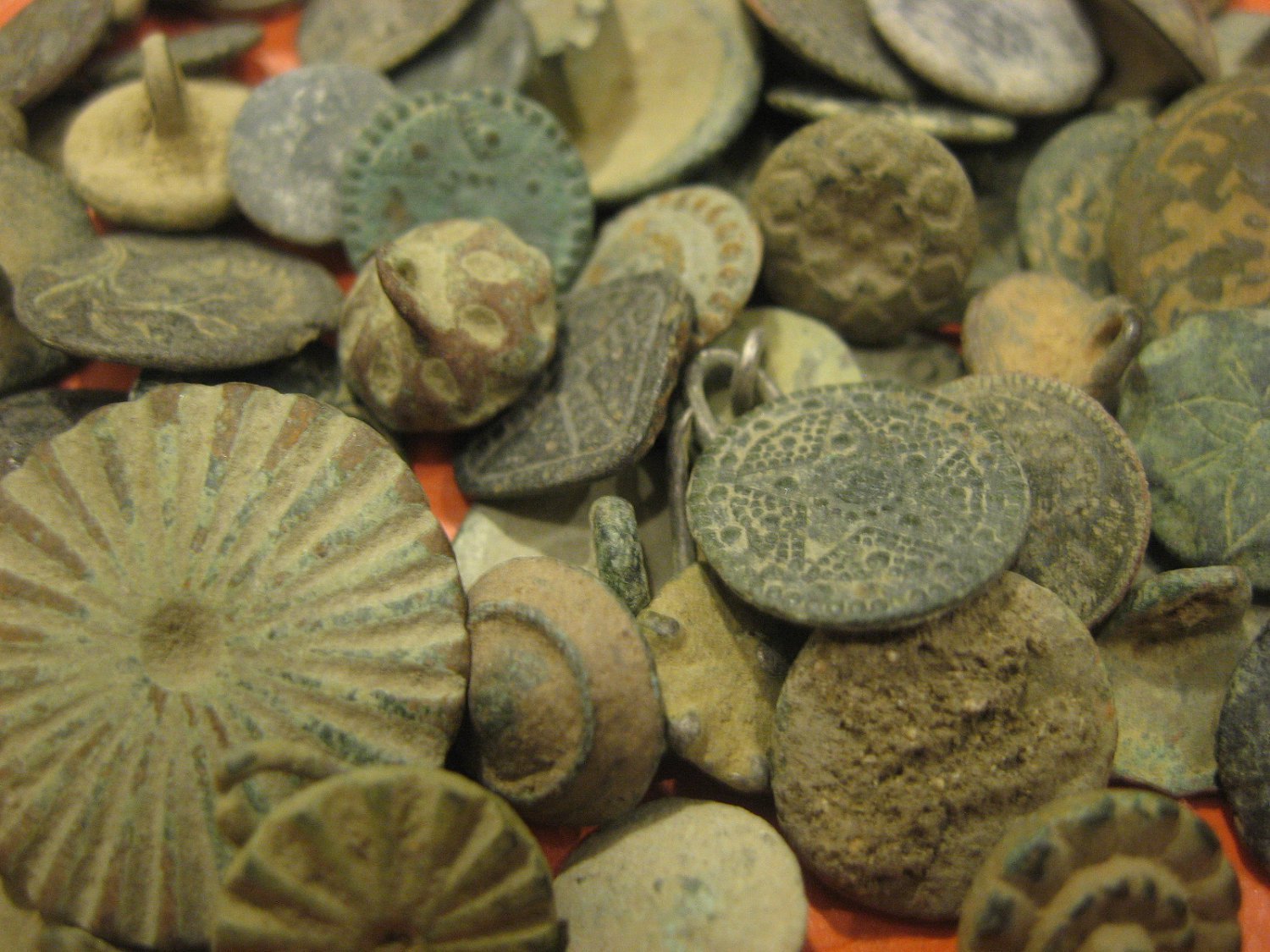
4. Indians were the first ones to use and invent buttons
Ornamental buttons made from seashell were used in the Indus Valley Civilization by 2000 BCE. Some buttons were carved into geometric shapes and had holes pierced into them.

5. Shampoo originated from India
The word shampoo is derived from Hindi word chāmpo and dates to 1762. The shampoo itself originated in the eastern regions of the Mughal Empire where it was introduced as a head massage, usually consisting of alkali , natural oils and fragrances. Shampoo was first introduced in Britain by a Bengali entrepreneur from Bihar named Sake Dean Mahomed.

6. India gave the c ure for Leprosy
Kearns & Nash (2008) state that the first mention of leprosy is described in the Indian medical treatise Sushruta Samhita (6th century BCE). However, The Oxford Illustrated Companion to Medicine holds that the mention of leprosy, as well as ritualistic cures for it, were described in the Atharva-veda (1500–1 200 BCE), written before the Sushruta Samhita .

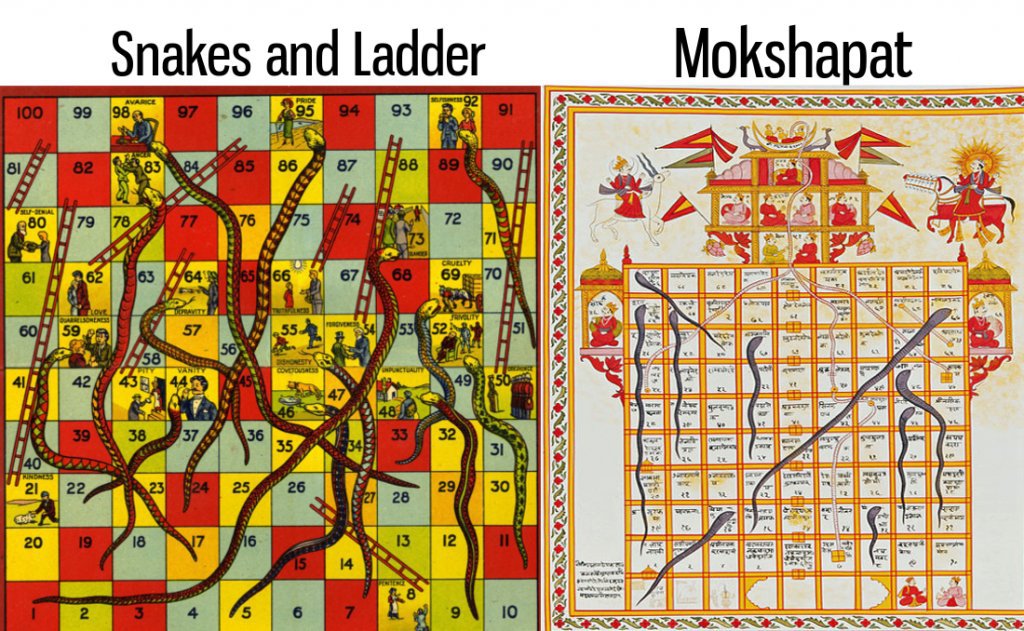
7. Snakes and Ladders was inspired from an Indian game called Mokshapat
It was originally called ‘ Mokshapat’. Snakes and ladders originated in India as a game based on morality. During British rule of India, this game made its way to England, and was eventually introduced in the United States of America in 1943.
8. Ayurveda originated from India
Ayurveda is an ancient system of medicine which dates back to Iron Age India (1st millennium BC) and is still practiced today as a form of complementary and alternative medicine .

9. Bhaskaracharya rightly calculated the time taken by the earth to orbit the sun
Using an astronomical model developed by Brahmagupta in the 7th century, Bhaskara accurately defined many astronomical quantities, including the length of the sidereal year, the time that is required for the Earth to orbit the Sun.
10. Buddhism and Jainism originated in India
Jainism has historically been largely confined to India , whereas Buddhism originated in India but subsequently flourished and developed several branches in other Asian countries.

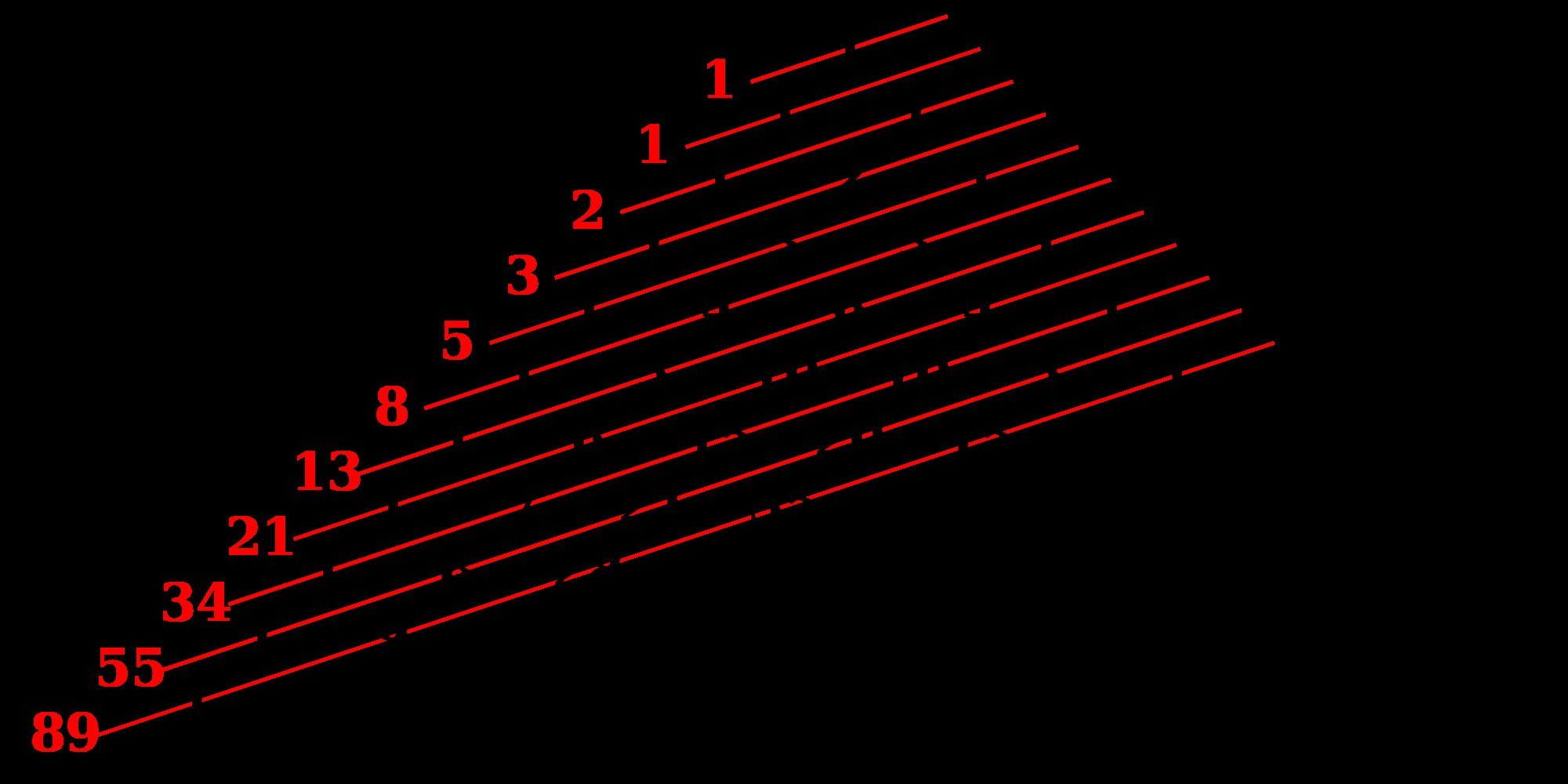
11. Indians were the first ones to describe the Fibonacci pattern of numbers
This sequence was first described by Virahanka (c. 700 AD), Gopāla (c. 1135), and Hemachandra as an outgrowth of the earlier writings on Sanskrit prosody by Pingala.
12. Cataract surgery was first found in ancient India
In India, cataract surgery was performed with a curved needle used to loosen the lens and push the cataract out of the field of vision. The eye would later be soaked with warm butter and then bandaged. Though this method was successful, Susruta cautioned that cataract surgery should only be performed when absolutely necessary. These methods were later spread tot he world.

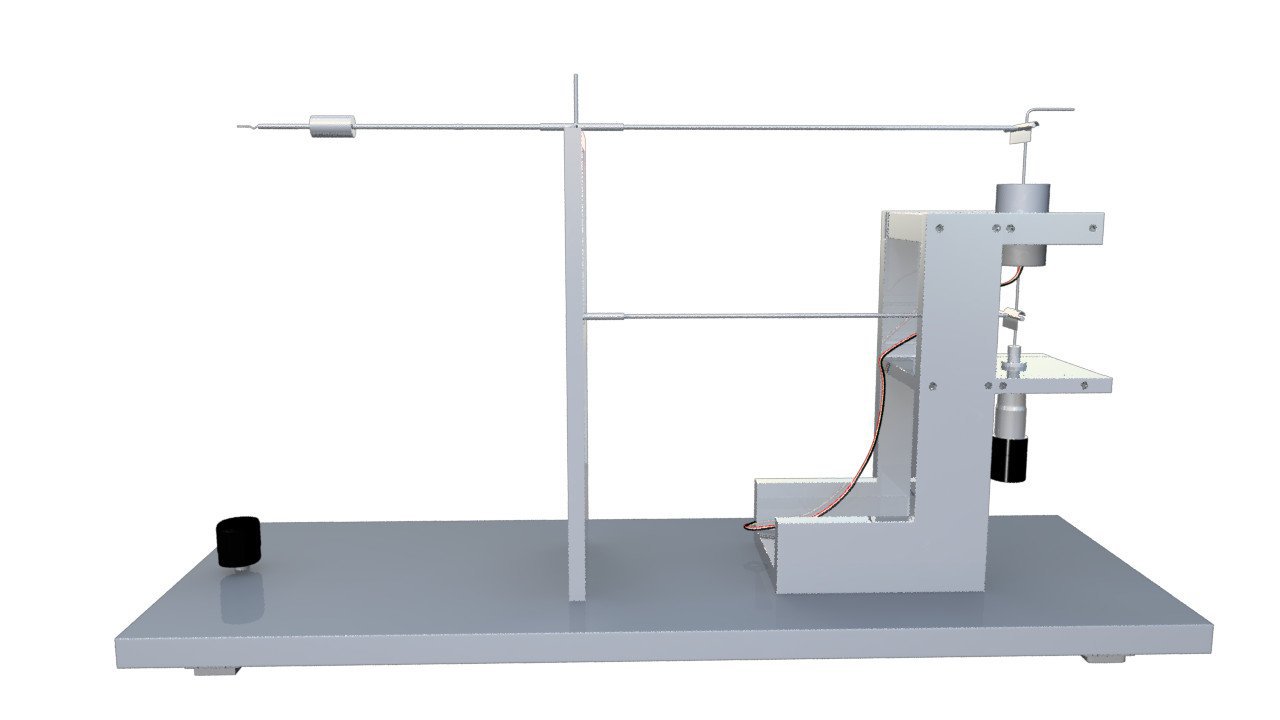
13. C rescograph is an Indian invention
It is a device for measuring growth in plants and was invented in the early 20th century by Sir Jagadish Chandra Bose.
14. Indians discovered the cashmere wool
The founder of the cashmere wool industry is traditionally held to be the 15th-century ruler of Kashmir, Zayn-ul-Abidin , who employed weavers from Central Asia . The mention of woolen shawls made from this wool in Kashmir are found in several books between 3rd century BCE and the 11th century CE.

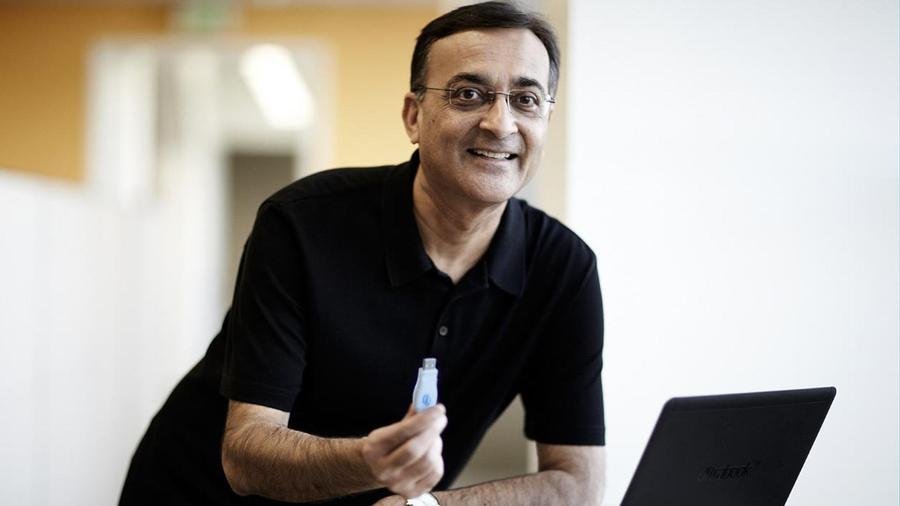
15. USB was developed and defined by Ajay V. Bhatt, who is an Indian-American computer architect
You can also credit him for AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) , PCI Express , Platform Power management architecture and various chipset improvements.

16. India invented card game called Suits
Kridapatram , which also means “painted rags for playing” is an early suits game, made of painted rags. It was invented in Ancient India.

17. India taught the world to cultivate Jute
Jute has been cultivated in India since ancient times. India also exported raw jute to the western world , where it was used to make ropes and cordage. The Indian jute industry was later modernized during the British Raj in India.

18. And described Trigonometric functions
The trigonometric functions sine and versine originated in Indian astronomy. They were described in detail by Aryabhatta in the late 5th century, but were likely developed earlier in astronomical treatises of the 3rd or 4th century. Later, the 6th-century astronomer Varahamihira discovered a few basic trigonometric formulas and identities, such as sin^2(x) + cos^2(x) = 1.
19. The Pentium Chip was invented by an Indian
Vinod Dham is also known as the Father of the Pentium chip, for his contribution to the development of highly successful Pentium processors from Intel.

20. India gave candied sugar to the world
The process of producing crystallized sugar from sugarcane was discovered by the time of the Imperial Guptas, and the earliest reference of candied sugar comes from India. The process was soon transmitted to China with traveling Buddhist monks. Chinese documents confirm two missions to India, for obtaining technology for sugar-refining.

So many reasons to be proud!

















