We all know that party and recreational drugs are harmful in the long run, but do we know what exactly these “foreign” substances are doing to the brain? Drugs stand at the confluence of reality and the “euphoric” dreamy state, often tricking our senses into perceiving a world different from what actually exists.
Here’s how these popular drugs affect our brain upon immediate administration:
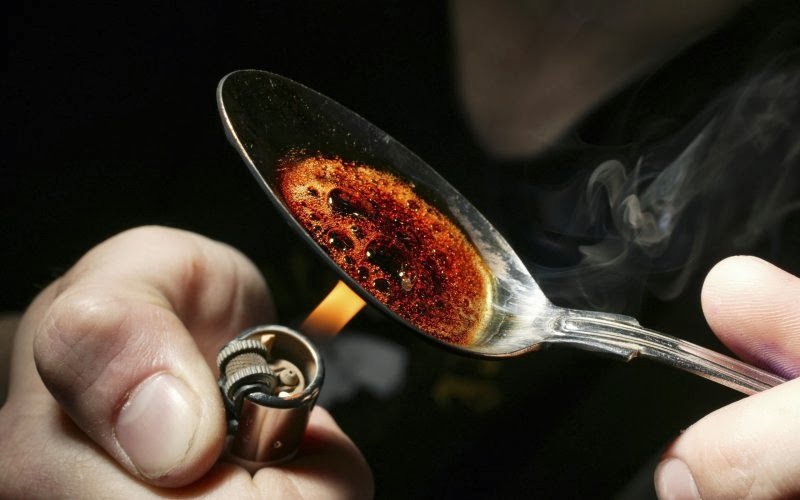
Heroin – Stops natural manufacture of dopamine
Heroin definitely plays on the brain’s perceptive powers. This drug constantly floods the body and the brain with extra opiates and dopamine. Dopamine is a chemical released by the brain that ensures healthy functioning and regulates emotion, perception and movement. When heroin is administered into the body, the brain gets used to it and is tricked to stop the natural manufacture of dopamine.
As a result, if regular users stop taking heroin, the “feel good” factor simply ceases to exist. They are unable to experience pleasure lest they take the drug. This is what leads to dependence on heroin.

LSD – Inhibits/Stimulates neurotransmission
The magical drug that fools people into believing that time is slowing down in addition to conjuring a kaleidoscopic imagery and at times a mystical experience, is a total psychological drug. It is believed that LSD works similarly to serotonin, which is a neurotransmitter responsible for regulating moods, muscle control, sleep and sensory perception. LSD interferes with the way the brain’s serotonin’s receptors function and inhibits/stimulates (either or both) neurotransmission. It also affects how the retinas process information, which explains the dancing patterns.

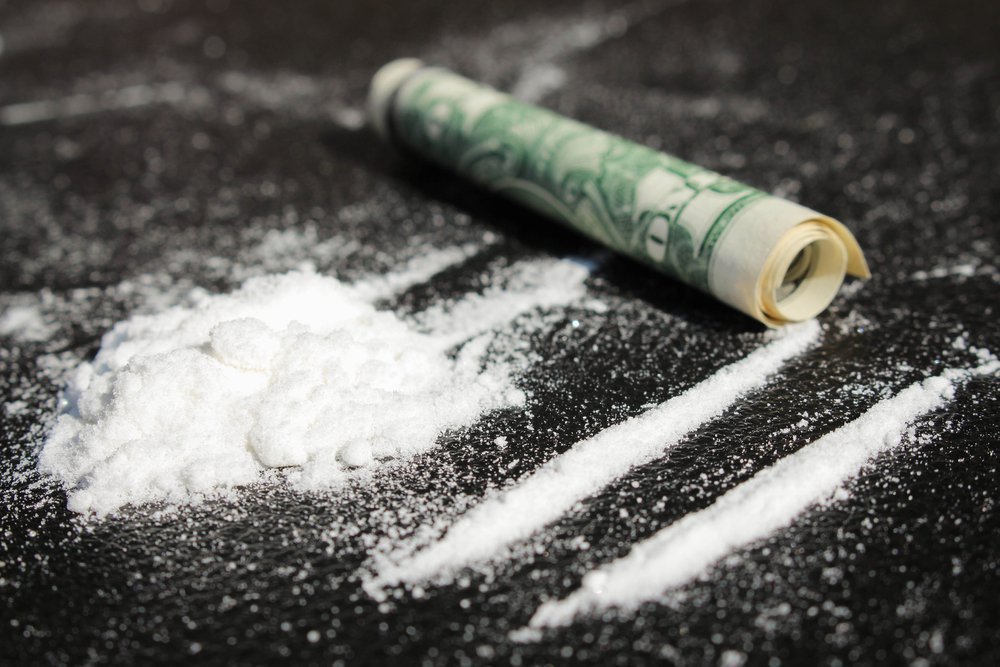
Cocaine – Disrupts the normal functioning of the brain
Cocaine is an extremely powerful central nervous system stimulant that greatly enhances levels of the neurotransmitter dopamine in brain circuits. In the usual course of action, dopamine is released by neurons in the brain circuits, in response to potential “rewards”, (for instance the smell of good food or a fragrance) and then recycled back into the cell that released it, thereby shutting off the signal between neurons.
Taking cocaine prevents the dopamine from being recycled, which amplifies the dopamine signals and ultimately disrupts normal brain communication. This excessive dopamine build up causes cocaine’s “characteristic” high!

DMT – Unnaturally releases neurotransmitter
You know what they say about DMT? “You should never go for it, but if it comes to you, you take it!”
This life-changing substance is also produced in our bodies by the pineal gland (debatable) and pumped out while we sleep (also debatable). DMT is said to bind to serotonin receptors in a manner that is similar to psilocin. As a result the neurons that would normally be triggered by the release of serotonin, are released without actual serotonin release. This spawns visual hallucinations and the feeling of being separated from reality, with users often reporting of “flying away” to another reality or paradigm.
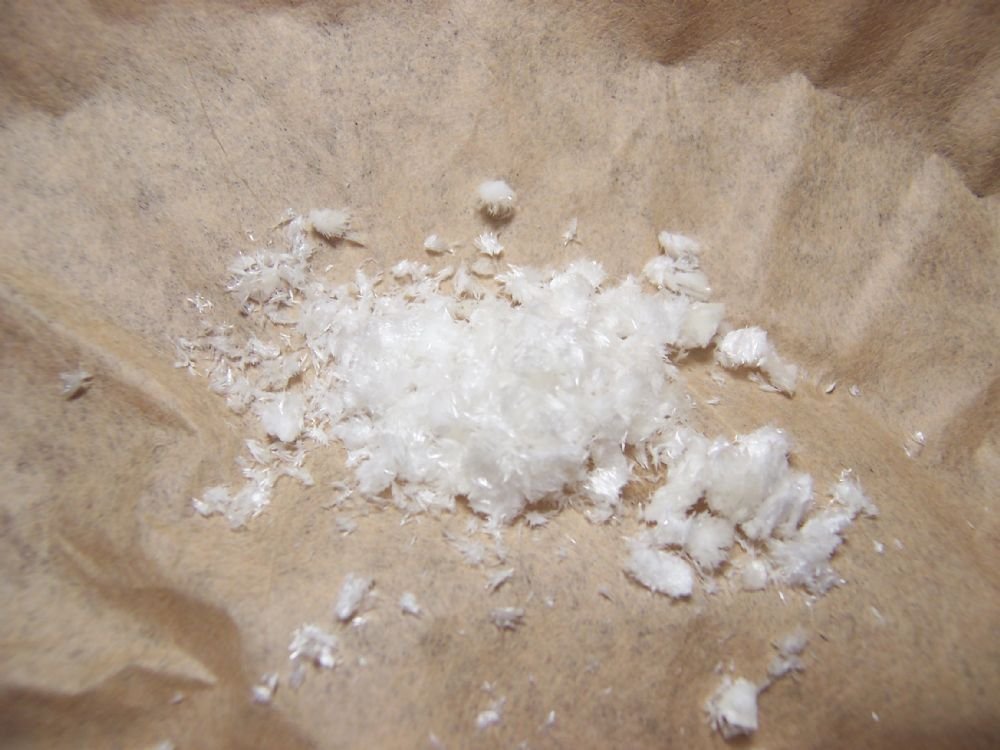

MDMA – enhances neurotransmitter activity
MDMA increases the activity of at least three neurotransmitters: dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin. The drug causes these neurotransmitters to be released from their storage sites in neurons, triggering enhanced neurotransmitter activity. The excess release courtesy MDMA is responsible for the mood-elevating effects. However, secretion of large amounts of serotonin (by MDMA) causes the brain to become significantly depleted of it, leading to negative behavioural after-effects for a few days.
Marijuana – keeps brain neurons active and fixated
Marijuana contains at least 60 types of cannabinoids (chemical compounds that act on receptors throughout the brain). THC or Tetrahydrocannabinol, the chemical compound responsible for the “euphoric high” resembles anandamide (naturally produced compound in the brain) that regulates mood, memory, sleep and appetite. Marijuana magnifies thoughts, perception and keeps the brain neurons active and fixated; which explains why Mary Jane boosts concentration/coordination.

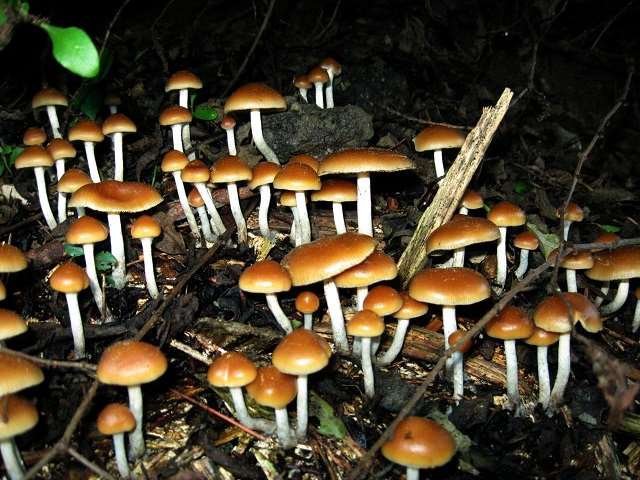
Shrooms – Boosts communication between different regions of the brain
Shrooms or “magic mushrooms” contain a chemical compound called psilocybin which causes users to experience a “sensory overload” of colours and patterns. Scientists claim that this is because of the brain’s ability to “hyperconnect” and boost communication between different regions. Scientists hope that this ability of theirs could actually go a long way in treating neurological conditions.


















