Recently, it was found that some greenish-black pigments have started to form on the walls of the Taj Mahal, that could possibly damage the iconic structure.

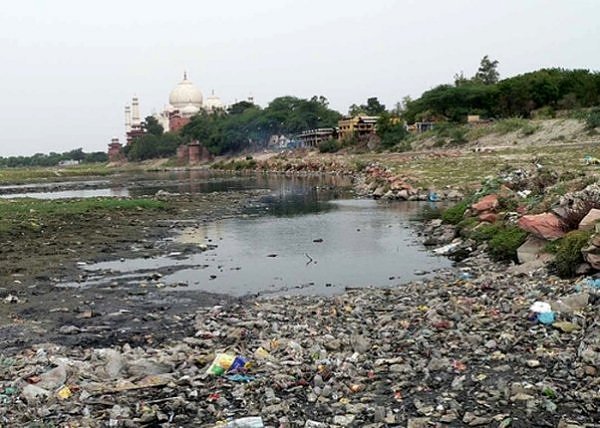
The prime reason was cited as the rampant dumping of municipal solid waste in Yamuna near Taj Mahal leading to stagnation of water in the river.
What are these green pigments?
The green pigments have been identified as Goeldichironomus by archaeologists. This particular species of pests grow near polluted water bodies. Yamuna river is currently serving as a breeding ground for the pests, according to a TOI report.
What could be the extent of damage?
According to Dr Girish Maheshvri, Head of Entomology Department at St John’s College, the insects are not likely to damage the marble stones of the Taj. They get attracted towards the white stone and start swarming towards it, which happens because of a nuptial fight among the pests.

What are authorities doing about the insect attack?
It has caught the attention of the National Green Tribunal which has sought reply from the Centre on the issue.
A bench headed by NGT Chairperson Justice Swatanter Kumar has issued notices to Ministry of Environment and Forests, Uttar Pradesh government, state pollution control board, State Environment Impact Assessment Authority and others.

The order came on the plea of environment activist and Agra resident D K Joshi who has claimed that dumping of waste in Yamuna has led to stagnation of the river and “consequently the explosive breeding of an insect called ‘Chironomus Calligraphus’ (Geoldichironomus), which is a biological indicator of water quality and localised water pollution.
The plea sought constitution of a Committee to look into the problem to prevent further damage to the river and the monument.

Taj Mahal is already reeling under pollution
This is not the first time such a concern has been raised for the iconic structure. There have been reports on how Taj is slowly turning brownish-yellow because of air pollution. Dust and carbon-containing particles emitted in the burning of fossil fuels, biomass and garbage were deposited on the structure.
(With inputs from PTI)