Get ready to have your minds blown, fellow Homo sapiens. There is some big news coming your way which may blow the lid off the mystery surrounding our evolution. No matter how much we discover about ourselves, history and science never cease to amaze us.
Explorers from the University of Witwatersrand, in a combined effort with National Geographic, have unearthed one of our ancestors who was more like us than any other . Fossils of Homo naledi, which might be 2 to 3 million years old , are believed to be that of the rich species of the Hominin lineage, found in a recovery of more individual remains than those found in South Africa over the last 90 years.
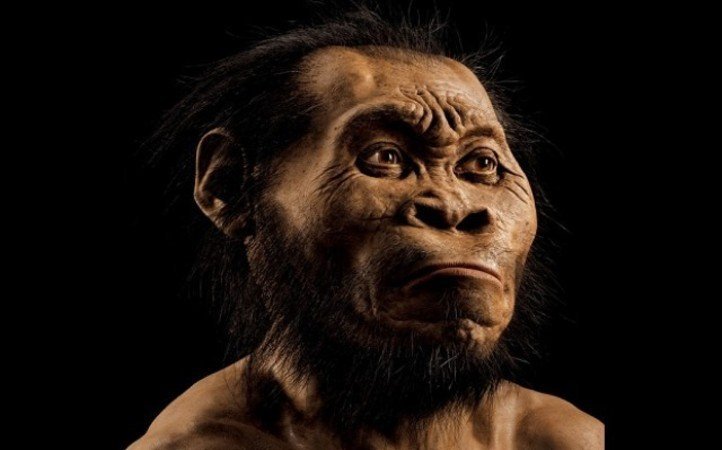

Burial rituals
Among many things it tells us about the human species, Homo naledi sheds light on the diversity that exists among us. It has also been seen as displaying a behavioural pattern which till now was seen exclusively as modern human behaviour — they disposed the bodies of their dead in a separate isolated and protected space.
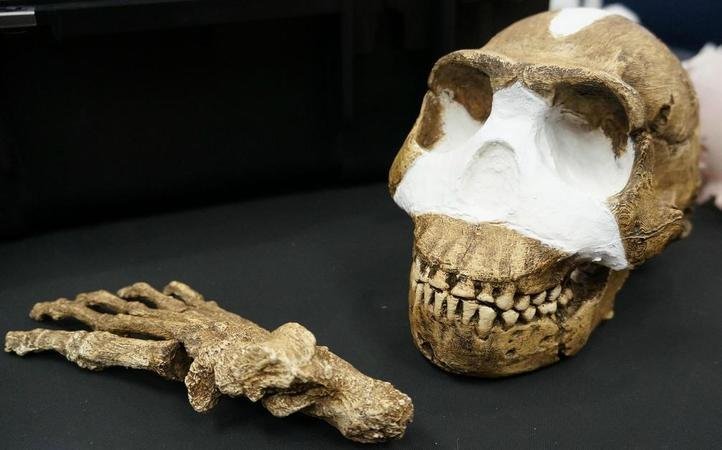
The location and the condition of the chamber, where 1500 remains belonging to 150 individuals were found, shows that Homo naledis braved travel by water and mass death to dispose of those who died.
This shows that either such practices have always been a part of the Hominid lineage or perhaps were invented by Homo naledi. That is mind blowing given the size of their brain which is a little more in size than that of a chimpanzee’s — orange-sized.
Closely related individuals
The team which first stumbled upon Homo naledi two years ago, thanks to an exploration by a group of amateur cavers called Rising Star, says that there might be thousands of remains since the floor is almost made up of bones. The fossils seem very similar to each other with little discrepancy between males and females, possibly belonging to different generations of a single family.
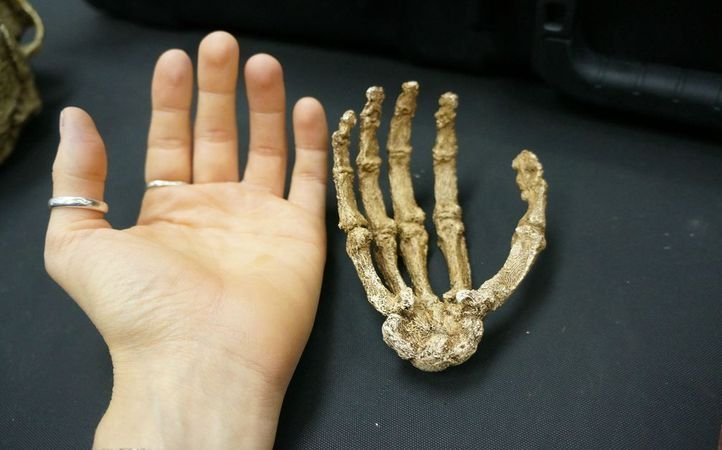
Human-like body structure
The new found Hominid is much taller as compared to earlier known species, and stands at 5 feet, which is not so tall when it comes to present-day humans. Naledi is a beautiful mix of modern humans and their primitive ancestors as far as features are concerned.
Some days, my job is REALLY cool…. #HomoNaledi pic.twitter.com/6Vcv3KEqbX
— Alex Eliseev (@alexeliseev) September 10, 2015 While the shoulder and pelvis appear primitive, hands and legs are almost identical to present day human beings. Apart from the burial rituals, not much is known about the actual behaviour of Homo naledi, whose name means star in the Sesotho language of South Africa. The fingers are more curved indicating that they were used to climb up something, which were definitely not just trees.
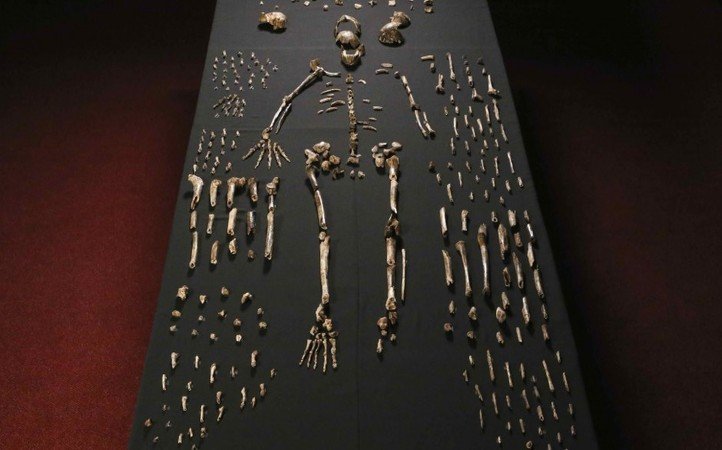
A Homo naledi assembled for display | Source: IFL Science